Energy-Efficient Window Frames: Comparing Materials
Windows play a crucial role in the overall energy efficiency of a building. They provide natural light and ventilation but can also be a significant source of energy loss if not properly designed and constructed. One key aspect of energy-efficient windows is the choice of window frames. The materials used for window frames have a substantial impact on a window’s insulating properties, durability, and overall performance. In this article, we will explore the various materials used for window frames and compare their energy efficiency, durability, and sustainability.
The Significance of Energy-Efficient Window Frames
Energy-efficient window frames are essential for several reasons:
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Windows can be a major source of heat gain in the summer and heat loss in the winter. Energy-efficient frames help minimize these losses, reducing the need for heating and cooling.
- Indoor Comfort: Well-insulated windows with energy-efficient frames help maintain a comfortable indoor environment by preventing drafts and temperature fluctuations.
- Lower Utility Bills: Improved energy efficiency leads to reduced energy consumption and lower heating and cooling costs, which can translate into significant savings over time.
- Environmental Impact: Energy-efficient window frames contribute to reducing a building’s carbon footprint by conserving energy and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Durability: High-quality window frames are built to last, reducing maintenance and replacement costs over the long term.
Common Materials for Window Frames
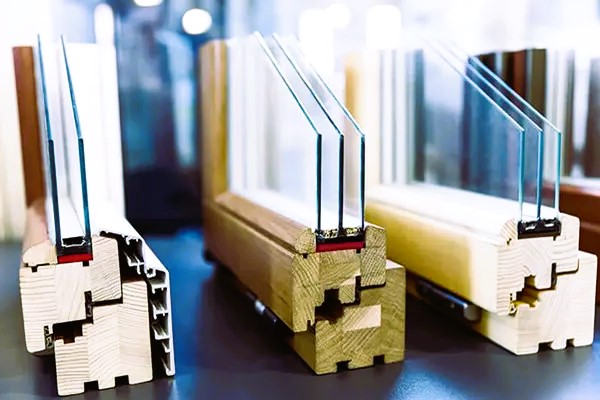

Several materials are commonly used for window frames, each with its unique properties and benefits. Here are some of the most common materials:
- Wood: Wood is a traditional and aesthetically pleasing choice for window frames. It offers natural insulation and has a classic, timeless look. However, wooden frames require regular maintenance to protect against rot and pests.
- Aluminum: Aluminum frames are known for their strength and durability. They are often used in commercial buildings and are lightweight, making them easy to install. However, aluminum is a conductor of heat and cold, which can lead to energy loss if not thermally broken.
- Vinyl: Vinyl window frames are low-maintenance, cost-effective, and offer good insulation properties. They are resistant to moisture, making them suitable for high-humidity environments. However, they may have limited color options and can be less visually appealing to some.
- Fiberglass: Fiberglass window frames are highly durable and provide excellent insulation. They are resistant to temperature fluctuations and require minimal maintenance. Fiberglass frames can be more expensive than other options.
- Composite: Composite frames are a blend of materials, typically a mixture of wood and vinyl or other polymers. They offer the advantages of both materials, including good insulation and low maintenance.
Comparing Energy Efficiency
The energy efficiency of window frames is often determined by their U-factor and R-value. The U-factor measures how well a window frame insulates, with lower values indicating better insulation. The R-value is the inverse of the U-factor, representing the window’s resistance to heat flow, with higher values indicating better insulation.
Here’s how different window frame materials compare in terms of energy efficiency:
- Wood: Wood frames can offer good insulation properties, with a U-factor typically ranging from 0.3 to 0.5. The natural insulating properties of wood contribute to its energy efficiency.
- Aluminum: Aluminum frames are less energy-efficient due to their high thermal conductivity. They have higher U-factors, typically ranging from 1.0 to 2.0. To improve their energy efficiency, some aluminum frames are thermally broken.
- Vinyl: Vinyl frames are energy-efficient, with U-factors ranging from 0.3 to 0.5. They offer good insulation and help reduce energy loss.
- Fiberglass: Fiberglass frames are highly energy-efficient, with U-factors similar to vinyl, ranging from 0.3 to 0.5. Their insulating properties contribute to excellent energy efficiency.
- Composite: Composite frames typically have U-factors in the same range as wood and vinyl, providing good energy efficiency. Interested in the topic of Renewable Energy in Nova Scotia? We have a lot of interesting things, more details here.
Durability and Sustainability
Durability and sustainability are also important factors to consider when choosing window frame materials:
- Wood: Wood frames can be durable if properly maintained. Sustainable wood sources and finishes can make wood frames an environmentally friendly choice.
- Aluminum: Aluminum frames are durable and resistant to corrosion. They are recyclable, making them an environmentally sustainable option.
- Vinyl: Vinyl frames are low-maintenance and have a long lifespan. They are often considered environmentally friendly due to their durability and recyclability.
- Fiberglass: Fiberglass frames are known for their durability and resistance to weathering. They are also considered environmentally friendly due to their long lifespan and recyclability.
- Composite: Composite frames combine the durability of materials like wood with the low maintenance of vinyl, offering a sustainable and long-lasting option.
Government Standards and Regulations

To ensure that window frames meet energy efficiency and safety standards, various government regulations and industry standards are in place. In Canada, organizations like the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) provide guidelines and standards for window frame materials to ensure they meet the necessary quality and safety requirements.
Conclusion
Choosing the right window frame material is a crucial decision when aiming for energy-efficient, durable, and sustainable windows. Each material has its advantages and considerations, and the choice may depend on factors such as budget, climate, and aesthetics. By considering the energy efficiency, durability, and sustainability of window frame materials, homeowners and builders can make informed decisions that contribute to energy conservation, comfort, and environmental responsibility.
For more information on energy-efficient window frames and relevant standards and regulations, you can refer to Canada.ca, where you can find valuable resources and guidelines. As we continue to prioritize energy efficiency and sustainability in building design, the choice of window frame materials plays a significant role in creating more eco-friendly and energy-efficient living spaces.