Heat Recovery Ventilators: Enhancing Indoor Air Quality
In an age where indoor living has become the norm for many people, ensuring good indoor air quality has never been more critical. The air we breathe indoors can be riddled with pollutants, allergens, and contaminants, which can have adverse effects on our health and well-being. This is where Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRVs) come into play. HRVs are innovative systems designed to enhance indoor air quality while also increasing energy efficiency in residential and commercial buildings. In this article, we will delve into the world of HRVs, exploring their function, benefits, and their role in improving the air we breathe indoors.
The Importance of Indoor Air Quality
Indoor air quality (IAQ) refers to the quality of air within and around buildings, especially concerning the comfort and health of the occupants. Poor IAQ can lead to various health issues, including allergies, asthma, and other respiratory problems. Common indoor pollutants and allergens include dust, pollen, pet dander, mold, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and more. Additionally, inadequate ventilation can lead to a buildup of carbon dioxide and moisture, creating an uncomfortable and potentially harmful environment.
The need to address IAQ has become more apparent in recent years, given the growing trend of tightly sealed, energy-efficient buildings. While these buildings are excellent at conserving energy, they can trap indoor pollutants and lead to poor IAQ if not properly ventilated.
What Are Heat Recovery Ventilators?
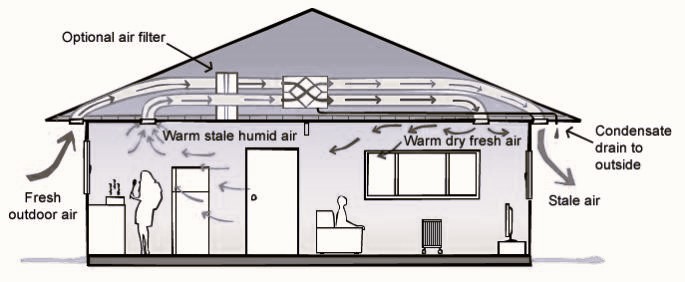
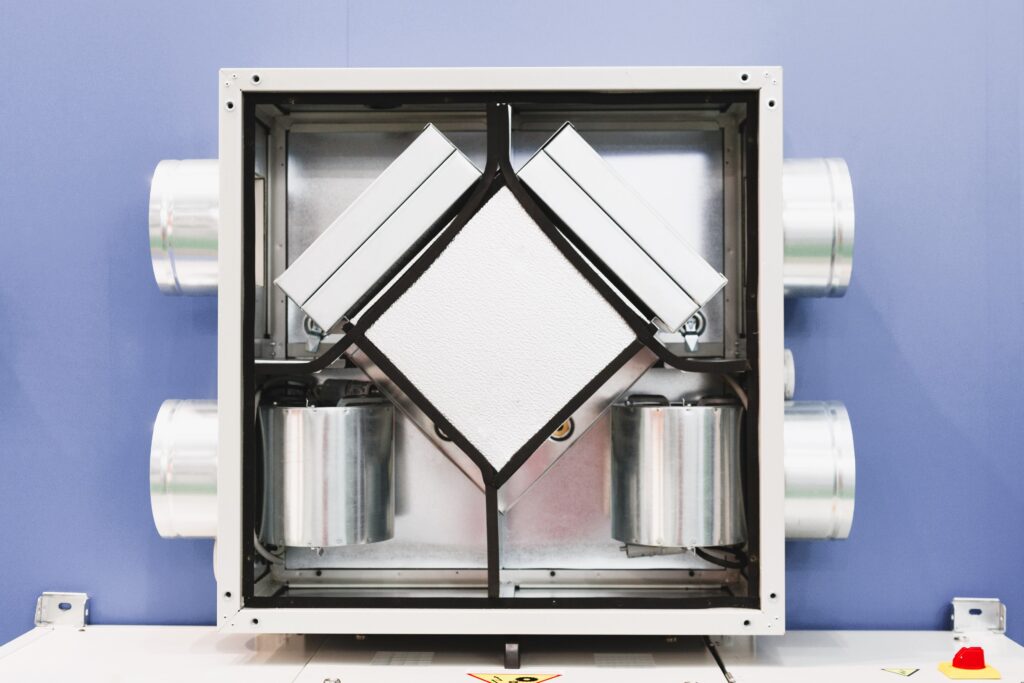
Heat Recovery Ventilators, often referred to as HRVs, are mechanical systems that facilitate the exchange of indoor and outdoor air in a controlled and energy-efficient manner. The primary function of HRVs is to provide fresh outdoor air while recovering heat from the exhausted indoor air. This heat exchange process not only ensures a constant supply of fresh air but also prevents the loss of heat, making HRVs an energy-efficient solution. Did you like the article? We also recommend that you familiarize yourself with Wood Pellet Stoves.
Here’s how HRVs work:
- Air Exchange: HRVs use a pair of fans to draw in fresh outdoor air and exhaust stale indoor air. These two airstreams pass through a heat exchanger.
- Heat Exchange: Within the heat exchanger, the heat from the outgoing indoor air is transferred to the incoming outdoor air. This preheats or pre-cools the incoming air, depending on the season, significantly reducing the energy required to heat or cool it.
- Balanced Ventilation: HRVs are designed to provide balanced ventilation, meaning that the volume of air leaving the building is equal to the volume of air entering it. This helps maintain the pressure balance within the building and ensures consistent indoor air quality.
Benefits of Heat Recovery Ventilators
The installation of HRVs offers numerous benefits for both residential and commercial buildings:
- Improved Indoor Air Quality: HRVs continuously provide a fresh supply of outdoor air, reducing the concentration of indoor pollutants and allergens. This leads to healthier and more comfortable indoor spaces.
- Energy Efficiency: HRVs recover heat from the outgoing air, which reduces the energy required for heating or cooling the incoming air. This can result in significant energy savings and lower utility bills.
- Condensation Control: Proper ventilation with HRVs helps control moisture levels in the indoor environment, preventing condensation on windows and walls. This can reduce the risk of mold growth and property damage.
- Enhanced Comfort: HRVs provide a consistent supply of fresh air, leading to improved comfort and well-being for occupants.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: By decreasing energy consumption and maintaining good indoor air quality, HRVs contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly living or working environment.
- Compliance with Building Codes: Many building codes and standards now require mechanical ventilation systems like HRVs to ensure good indoor air quality and energy efficiency.
Types of Heat Recovery Ventilators
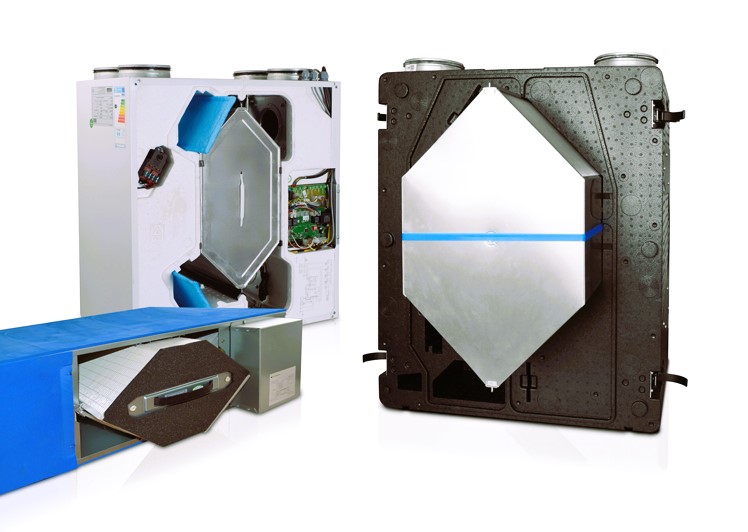

There are several types of HRVs available, each with its unique features and applications:
- Plate Heat Exchanger HRVs: These are the most common and cost-effective type of HRVs. They use a flat, cross-flow heat exchanger made of thin metal plates to transfer heat between the incoming and outgoing air streams.
- Rotary Heat Exchanger HRVs: Rotary HRVs use a rotating wheel with a desiccant to transfer heat and moisture between air streams. These HRVs are highly efficient but can be more expensive.
- Run-Around Coil HRVs: This type of HRV uses a pair of coils and a circulating fluid (typically water or refrigerant) to transfer heat between the incoming and outgoing air streams. Run-around coil HRVs are often used in larger, commercial applications.
Government Standards and Regulations
To ensure the effectiveness and safety of HRVs, various government standards and regulations are in place. In Canada, for instance, the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) has established standards for HRVs, covering their design, performance, and safety. Compliance with these standards is crucial to ensure that HRVs meet the necessary quality and safety requirements.
Conclusion
Heat Recovery Ventilators (HRVs) are a vital component of modern building systems that address the dual challenge of energy efficiency and indoor air quality. By providing a continuous supply of fresh air while recovering heat from the outgoing air, HRVs offer a sustainable and cost-effective solution for residential and commercial buildings.
For more information on HRVs, energy efficiency, and building standards, you can refer to Canada.ca, where you can find valuable resources and guidelines. As we continue to focus on creating healthier and more energy-efficient indoor environments, HRVs play a crucial role in enhancing our quality of life and promoting a sustainable future.