The Connection Between Window Upgrades and Energy Savings
Windows are not just mere openings that allow light and fresh air into our homes. They play a crucial role in the energy efficiency of a building. The quality, type, and condition of your windows can significantly impact your energy consumption and, consequently, your energy bills. In this article, we will explore the intricate connection between window upgrades and energy savings, shedding light on how making the right choices can lead to a more sustainable and cost-effective home.
Understanding the Importance of Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency has become a global concern, driven by the need to reduce energy consumption and combat climate change. Buildings, both residential and commercial, are responsible for a significant portion of energy usage and greenhouse gas emissions. Improving the energy efficiency of a building not only reduces energy bills but also lowers its environmental footprint.
Windows are one of the key components in building design that can either enhance or hinder energy efficiency. They can impact energy savings in several ways:
- Insulation: Windows can lose or gain heat, depending on their insulation properties. Properly insulated windows can prevent heat from escaping during the winter and block excessive heat from entering during the summer.
- Daylighting: Energy-efficient windows allow more natural light into a building, reducing the need for artificial lighting and its associated energy consumption.
- Solar Heat Gain: The ability of windows to control the amount of solar heat entering a building is crucial. In colder climates, you want windows that let in sunlight to warm your interior. In warmer climates, you need windows that block excessive solar heat.
- Ventilation: Windows that can be opened provide natural ventilation, reducing the need for mechanical cooling systems.
The Connection Between Window Upgrades and Energy Savings

Upgrading your windows can have a profound impact on your home’s energy efficiency and, by extension, your energy savings. Here’s how the two are interconnected:
- Improved Insulation: Old or poorly insulated windows can be a significant source of heat loss during the winter and heat gain during the summer. Upgrading to energy-efficient windows with double or triple glazing, low-emissivity coatings, and gas fills can dramatically improve insulation, reducing the need for constant heating or cooling. This, in turn, leads to substantial energy savings.
- Lower Energy Bills: When your home is better insulated and retains heat more effectively, your heating and cooling systems won’t have to work as hard. As a result, you’ll see a significant reduction in your energy bills. Interested in green heating? Read also about Heat recovery fans: improving indoor air quality.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Energy-efficient windows can help lower your carbon footprint by reducing your energy consumption. Less energy usage means fewer greenhouse gas emissions, which is a positive step towards mitigating climate change.
- Enhanced Comfort: Upgraded windows not only save energy but also improve the comfort of your home. You’ll experience fewer drafts and temperature variations, creating a more pleasant living environment.
- Long-Term Savings: While the initial cost of upgrading windows may seem significant, the long-term savings in energy bills often outweigh the investment. The return on investment (ROI) in energy savings can be quite compelling.
- Increased Property Value: Energy-efficient upgrades, including high-quality windows, can increase the value of your property. Potential buyers appreciate the lower operating costs and the positive environmental impact.
Government Standards and Regulations
Government standards and regulations play a vital role in the promotion of energy-efficient window upgrades. In Canada, for example, there are specific energy codes and standards that windows must meet to ensure their energy efficiency. The Canadian Standards Association (CSA) is a key organization responsible for setting and maintaining these standards.
Additionally, government incentives and rebates are often available to encourage homeowners to make energy-efficient upgrades, including window replacements. These incentives can further offset the upfront costs and accelerate the return on investment.
Types of Energy-Efficient Windows
When considering window upgrades for energy savings, it’s essential to be aware of the various types of energy-efficient windows available:
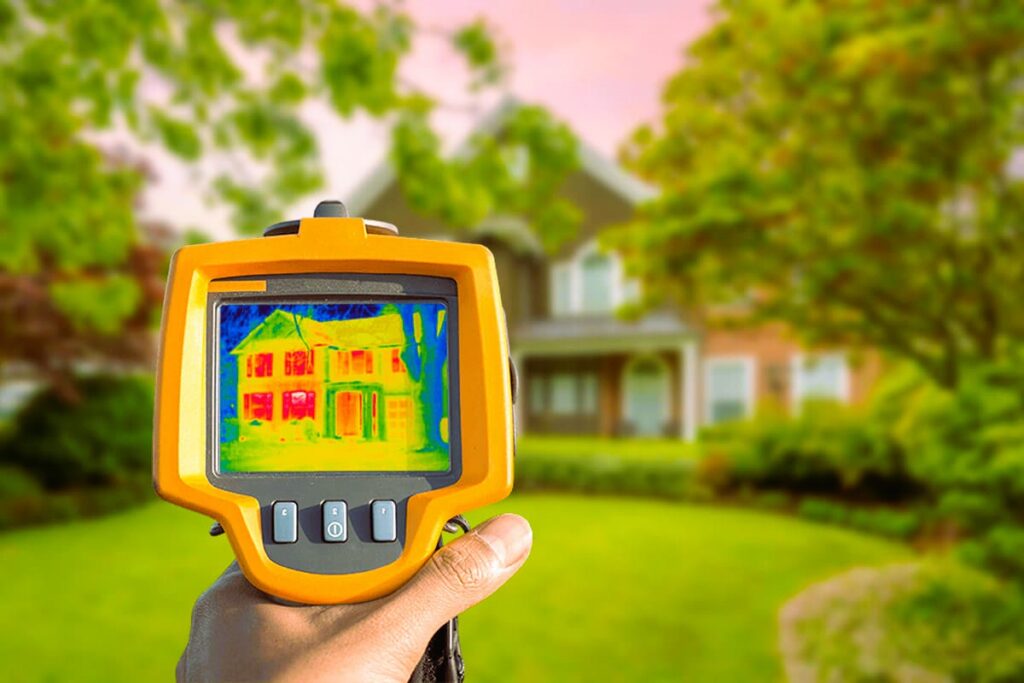

- Double-Glazed Windows: These windows have two layers of glass with an insulating air space in between. They provide better insulation than single-pane windows.
- Triple-Glazed Windows: Triple-glazed windows have three layers of glass with two insulating air spaces. They offer even higher levels of insulation.
- Low-E Coatings: Low-emissivity coatings are thin, invisible layers applied to the glass surface. They reduce heat transfer while allowing visible light to pass through.
- Gas Filled Windows: Some energy-efficient windows are filled with insulating gases like argon or krypton, which further reduce heat transfer.
- ENERGY STAR® Windows: Look for windows that carry the ENERGY STAR label, indicating they meet or exceed specific energy efficiency criteria established by the Canadian government.
Conclusion
The connection between window upgrades and energy savings is undeniable. By investing in energy-efficient windows, you can improve insulation, reduce energy bills, lower your carbon footprint, and enhance the overall comfort of your home. With the support of government standards, regulations, and incentives, upgrading your windows becomes an accessible and cost-effective way to contribute to a more sustainable and energy-efficient future.
For more information on energy-efficient window standards and regulations in Canada, you can visit the official Canada.ca website for detailed guidance on energy efficiency and sustainable building practices. Making the right choice for your windows can lead to a brighter, more energy-efficient future for your home and the environment.