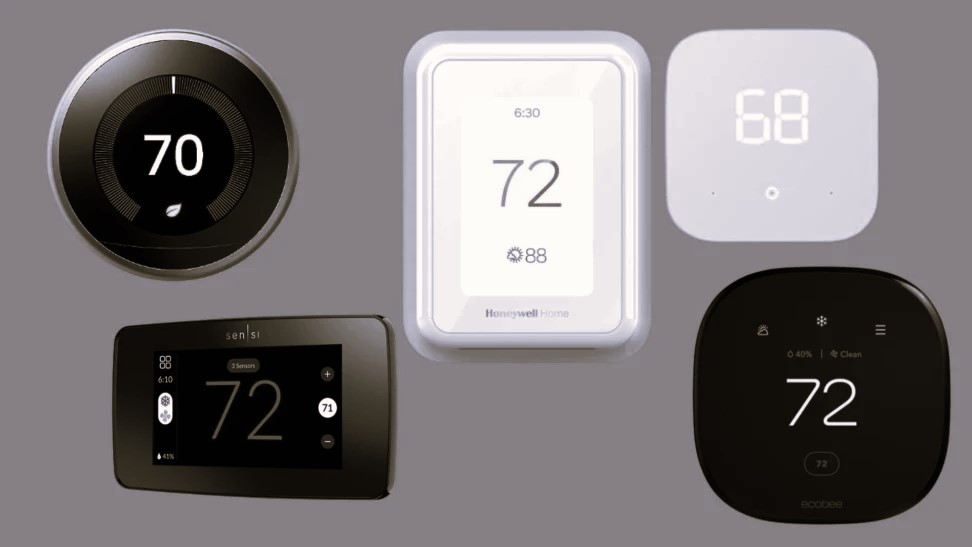
Smart Thermostats: Precision Control for Eco-Friendly Heating
In an age of increasing environmental awareness and the need for energy conservation, the role of smart technology in shaping our homes has never been more prominent. One of the key players in this shift towards energy-efficient living is the smart thermostat. These intelligent devices provide precision control over heating and cooling systems, resulting in eco-friendly and cost-effective solutions for managing indoor temperatures. In this article, we will explore the world of smart thermostats, their functionality, benefits, and their vital role in creating sustainable and comfortable living spaces.
The Evolution of Home Heating
Heating and cooling our homes have come a long way from traditional wood-burning stoves and manually controlled thermostats. The advancement of technology, coupled with environmental concerns, has driven the development of smart thermostats. These devices represent a significant step towards achieving energy-efficient and eco-friendly heating solutions.
Smart thermostats are designed to provide homeowners with precise control over their HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems. They offer a range of features and capabilities that enable users to optimize their heating and cooling while minimizing energy consumption.
How Smart Thermostats Work

Smart thermostats work through a combination of sensors, algorithms, and user inputs to regulate indoor temperatures efficiently. Here’s a simplified breakdown of their operation:
- Sensors: Smart thermostats are equipped with various sensors that monitor conditions in and around your home. These sensors can include temperature sensors, humidity sensors, occupancy sensors, and even outdoor weather data.
- Data Collection: The sensors continuously collect data and feed it to the thermostat’s internal processor.
- Algorithmic Control: The thermostat’s algorithms process the collected data and make decisions on how to maintain the desired indoor temperature. These decisions are based on factors like occupancy, outdoor weather conditions, and historical usage patterns.
- User Interface: Smart thermostats typically offer user-friendly interfaces, which can be accessed through smartphone apps or web interfaces. Users can set schedules, adjust temperature settings remotely, and receive energy usage reports.
- Learning Capabilities: Some smart thermostats have learning capabilities and can adapt to user preferences over time. They can “learn” your schedule and make automatic adjustments to save energy.
- Remote Connectivity: Many smart thermostats are Wi-Fi-enabled, allowing users to control their HVAC systems remotely, which can be especially convenient for homeowners who want to ensure their homes are comfortable when they return. Energy-efficient window frames, in the article we made a comparison of materials.
Benefits of Smart Thermostats
The adoption of smart thermostats offers a multitude of benefits for homeowners and the environment:
- Energy Savings: By optimizing heating and cooling, smart thermostats can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower utility bills. They can prevent overheating or overcooling of spaces when occupants are absent.
- Environmental Impact: Lower energy consumption means reduced carbon emissions, contributing to a more sustainable and eco-friendly living environment.
- Precision Control: Smart thermostats allow for precise temperature control, ensuring that your home is consistently comfortable.
- Convenience: Remote access and control via smartphone apps provide convenience and flexibility for homeowners.
- Learning Capabilities: Some models can learn from your temperature preferences and automatically create efficient heating and cooling schedules.
- Compatibility: Smart thermostats are often compatible with a wide range of HVAC systems, making them suitable for various home setups.
- Feedback and Reports: Many smart thermostats provide detailed energy usage reports and feedback, allowing users to track their consumption and make informed decisions.
- Zoning: Some systems support zoning, enabling users to control temperatures in different areas of their homes independently.
Government Standards and Regulations

Government standards and regulations in Canada, for example, focus on promoting energy efficiency and sustainable living practices. These standards may include guidelines on energy-efficient HVAC systems, which are often part of the building code.
The Canadian Standards Association (CSA) is a key organization responsible for setting and maintaining standards related to heating, cooling, and HVAC systems. Compliance with these standards is crucial to ensure that smart thermostats and HVAC systems meet the necessary quality and safety requirements.
Conclusion
Smart thermostats offer precision control over heating and cooling, allowing homeowners to create eco-friendly, comfortable, and energy-efficient living spaces. By leveraging advanced technology, these devices contribute to the reduction of energy consumption, lower utility bills, and reduced carbon emissions. As we continue to prioritize sustainability and environmental responsibility, smart thermostats play a pivotal role in enhancing our living spaces and reducing our carbon footprint.
For more information on smart thermostats and relevant standards and regulations in Canada, you can refer to Canada.ca, where you can find valuable resources and guidelines. The adoption of smart thermostat technology is a significant step towards creating a more sustainable and eco-friendly future for our homes and the environment.