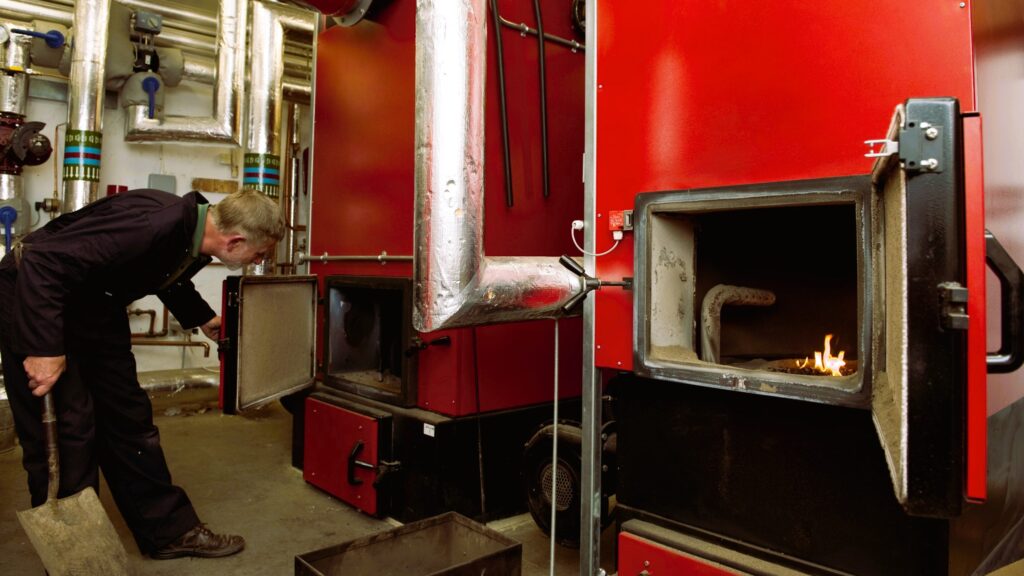
Biomass Heating: A Sustainable Approach to Warming Your Home
In the age of environmental awareness and sustainable living, finding eco-friendly ways to heat our homes has become a priority. Biomass heating is one such solution that offers a sustainable and renewable approach to keeping our homes warm and comfortable. This article will delve into the world of biomass heating, exploring what it is, how it works, and why it’s considered a green alternative to traditional heating methods.
Understanding Biomass Heating
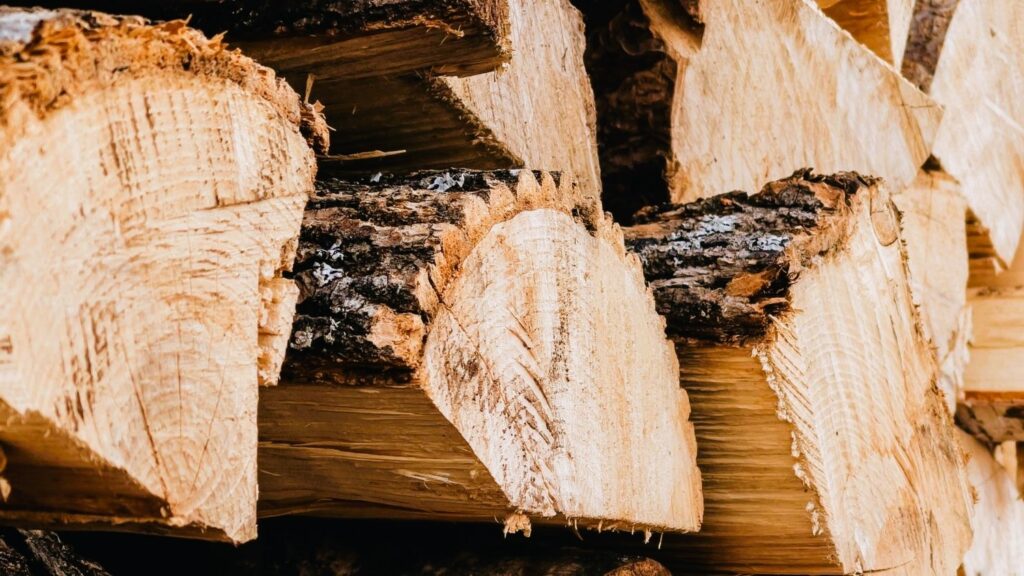
Biomass refers to organic materials derived from plants and animals. It includes a wide range of materials, such as wood, agricultural residues, and even certain types of algae. Biomass heating systems utilize these organic materials to generate heat for various purposes, including residential heating. Let’s take a closer look at the key elements of biomass heating:
1. Fuel Types: Biomass heating systems can use a variety of fuels, including wood chips, wood pellets, agricultural residues like corn stalks, and energy crops like switchgrass. The choice of fuel depends on availability and regional factors.
2. Combustion Process: Biomass fuels are burned in a combustion chamber to produce heat. This heat can then be used for space heating, water heating, and more. The combustion process is designed to be highly efficient and produce minimal emissions.
3. Sustainability: Biomass is considered a sustainable energy source because the carbon dioxide (CO2) released during combustion is roughly equal to the CO2 absorbed by the plants during their growth. This carbon neutrality makes biomass heating an environmentally responsible choice.
Environmental Benefits of Biomass Heating

Biomass heating systems offer several compelling environmental advantages:
1. Carbon Neutrality: As mentioned earlier, the carbon dioxide emitted during biomass combustion is offset by the CO2 absorbed by the plants during their growth. This balance makes biomass heating carbon neutral and helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Reduction of Waste: Biomass fuels often consist of agricultural residues or wood byproducts that would otherwise go to waste. By using these materials as fuel, biomass heating contributes to waste reduction and resource utilization.
3. Local Sustainability: Biomass fuels can be sourced locally, supporting regional economies and reducing transportation-related emissions. For more information on how to choose energy-efficient windows for your climate, follow the link.
Types of Biomass Heating Systems
There are various types of biomass heating systems, each with its own unique features and advantages:
1. Wood Pellet Stoves: These stoves burn compressed wood pellets, providing a convenient and efficient way to heat a home.
2. Wood Chip Boilers: Wood chips are used as fuel in central heating systems, making them suitable for larger homes or buildings.
3. Pellet Boilers: Similar to wood chip boilers, pellet boilers use wood pellets as a fuel source and are highly automated.
4. Biomass Furnaces: Biomass furnaces can use a variety of fuels, including wood chips and agricultural residues, to produce hot air for heating.
5. Combined Heat and Power (CHP) Systems: These systems not only generate heat but also produce electricity, making them highly efficient and versatile.
Government Support and Incentives
To promote the adoption of biomass heating systems and other renewable energy solutions, governments worldwide, including the Canadian government, offer various support programs and incentives. Homeowners may be eligible for rebates, tax credits, and grants to offset the cost of installing biomass heating systems.
For detailed information on government programs and incentives in Canada, you can visit the official website of the Government of Canada.
Considerations for Biomass Heating

While biomass heating offers numerous environmental and economic benefits, there are some factors to consider:
1. Fuel Availability: The availability of biomass fuels in your region will impact the feasibility of biomass heating. It’s essential to have a consistent and affordable supply of biomass fuel.
2. Maintenance: Biomass heating systems may require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
3. Efficiency: The efficiency of a biomass heating system can vary depending on the design and fuel source. It’s important to choose a system that meets your specific needs.
Conclusion
Biomass heating represents a sustainable and environmentally responsible approach to warming your home. By utilizing organic materials that are readily available and carbon-neutral, biomass heating reduces greenhouse gas emissions, supports local economies, and minimizes waste. With government incentives and a growing focus on renewable energy, biomass heating is becoming an increasingly attractive choice for homeowners looking to embrace sustainability while staying warm and cozy.